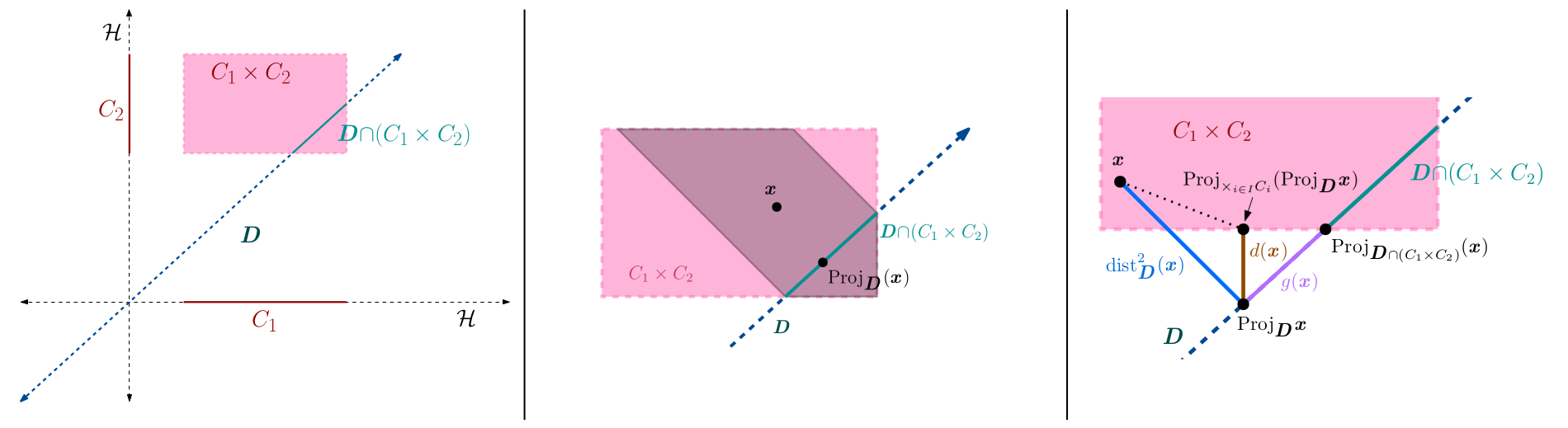
We propose a novel generalization of the conditional gradient (CG / Frank-Wolfe) algorithm for minimizing a smooth function $f$ under an intersection of compact convex sets, using a first-order oracle for $\nabla f$ and linear minimization oracles (LMOs) for the individual sets. Although this computational framework presents many advantages, there are only a small number of algorithms which require one LMO evaluation per set per iteration; furthermore, these algorithms require $f$ to be convex. Our algorithm appears to be the first in this class which is proven to also converge in the nonconvex setting. Our approach combines a penalty method and a product-space relaxation. We show that one conditional gradient step is a sufficient subroutine for our penalty method to converge, and we provide several analytical results on the product-space relaxation’s properties and connections to other problems in optimization. We prove that our average Frank-Wolfe gap converges at a rate of $\mathcal{O}(\ln t/\sqrt{t})$, – only a log factor worse than the vanilla CG algorithm with one set.
Slides from an early talk on this article are here.